Egg White Types
DRIED EGG WHITE
By having most of the moisture removed, dried egg whites are viewed as more convenient than fresh or liquid egg whites, as the dried version has a longer shelf life and is shelf stable. Dried egg white also readily reconstitutes and easily blends with other dry ingredients.
Dried egg white manufacturing in the United States is defined in 21CFR160.145; however, the U.S. standard does not specify minimum or maximum moisture contents. Dried egg whites are usually produced by spraying atomized liquid egg white into a heated drier chamber. A continuous flow of accelerated heated air removes most of the moisture. The resulting ingredient is referred to as spray-dried egg white, spray-dried egg white solids or spray-dried egg albumen. Egg white can also be dried on trays or pans to create a flake or granular form.
Glucose, a reducing sugar, is removed from egg whites before drying to produce product with excellent storage stability. Whipping aids such as sodium lauryl sulfate may be added to dried egg white products at less than 0.1 percent by weight of the liquid prior to drying. Dried egg white with sodium lauryl sulfate is often referred to as high-whip dried egg white.
Food manufacturers use dried egg whites in a variety of applications including frozen desserts, bakery mixes, meringues, coatings and batters. For example, dried egg white, in combination with dried milk, flour and seasonings has been shown to make an excellent batter for deep-frying vegetables, meat and seafood. Egg white foams increase six to eight times in volume, and along with the gluten and starch in flour, establish the basic structure for angel food cakes. Dried egg white is also used in white cake formulas. Reconstituted dried egg white can be brushed on top of breads and other bakery products, acting like an adhesive for toppings such as seeds. The egg white also produces a light, shiny surface.
REFRIGERATED LIQUID/FROZEN EGG WHITE
Egg white, also referred to as egg albumen, contains 56 percent of the whole egg’s total protein along with the majority of the egg’s niacin, riboflavin, choline, magnesium, potassium, sodium and sulfur.
Alone, egg whites are about 88 percent water, 10 percent protein and almost completely free of fat and cholesterol, making it a very attractive ingredient in today’s food formulating industry. In fact, egg whites are a high‐quality, nutrient dense food ingredient, as the protein in egg white has a very high biological value. It has also been shown to provide satiety and thus assist in weight loss diets.
The proteins in egg whites are very functional, and assist food product developers with overcoming certain formulating challenges. An increasingly popular challenge in today’s food industry is to satisfy the restrictions set by natural foods stores on what a product may or may not contain. Egg whites have always been a good choice, as it is all‐natural and a nutrition powerhouse.
Egg whites help formulators with producing high‐volume foams and with leavening. When combined with other ingredients such as water or milk, it can be used to glaze pocket‐style sandwiches, rolls and breads, preventing the crusts from drying. Egg whites also act as an adhesive in both breading and coating processes, as well as with topical application of nuts and seeds.
For ease of convenience, egg product manufacturers separate egg whites from egg yolks, and sell them as individual ingredients. Liquid egg whites are available refrigerated, ready‐to‐use, or frozen. The advantage to frozen egg whites is a lengthier shelf life. Food manufacturers can thaw and use on an as-needed basis.
Regardless if liquid egg whites are sold refrigerated or frozen, they are always pasteurized for safety. Egg whites can also be formulated to include other ingredients such as salt or sugar for added shelf life and enhanced functionality. At the industrial level, liquid white—refrigerated or thawed frozen—can be added with other wet ingredients. Liquid whites readily integrate into manufacturing systems, including pumping and extrusion.
AVAILABILITY
DRIED EGG WHITE
- High-Whip Egg White Solids
- Instant Egg White Solids
- Pan Dried Albumen
- High-Gel Egg White Solids
REFRIGERATED LIQUID/FROZEN EGG WHITE
- Egg White
- Salted Egg White
- Extended Shelf Life Egg White
- High-Gel Egg White
- High-Whip Egg White
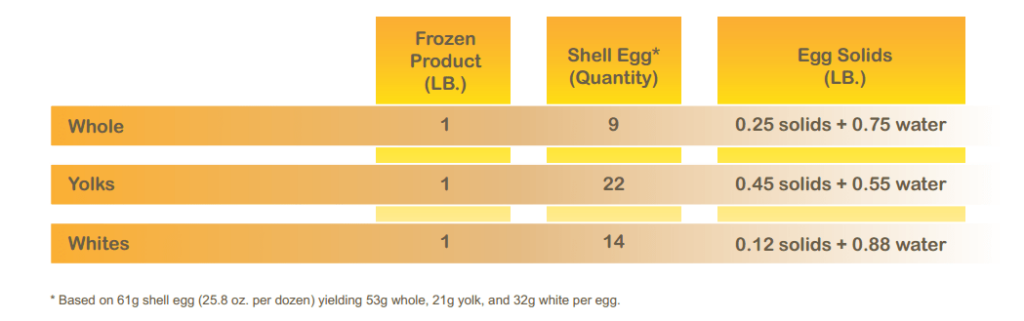
PRODUCT CONVERSION
Use this chart to convert refrigerated/frozen egg products to shell or dried egg products.
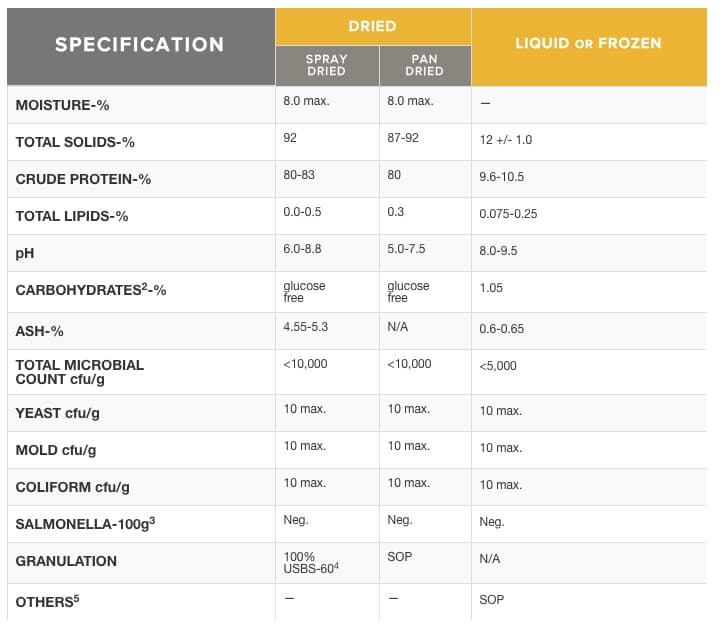
Egg White Specifications
References
- Free-flowing products contain less than 2% sodium silicoaluminate.
- Most dried egg whites are desugared. Whole egg and yolk products are desugared if specified on purchase (SOP).
- Negative by USDA approved testing procedures.
- U.S. Bureau of Standards.
- Additives and performance specifications may be specified on purchase.
